- KAKEN TEST CENTER
- SERVICES
- TESTING and INSPRCTION
Color fastness
Outline and judgment of Color fastness (JIS L 0801)
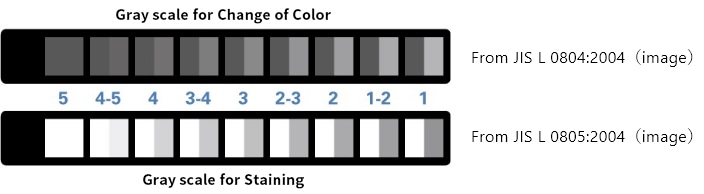
The "Color fastness test" evaluates "discoloration/fading (color change) " and "color transfer (staining) to other fabrics" such as dyes used in fabrics. JIS L 0803 standard adjacent white fabric is used for evaluation of staining.
Grayscale is used to determine dye fastness. The test pieces that have undergone various color fastness tests are compared using the gray scale as the standard and the evaluation is graded from 5th grade to 1st grade. The higher the number, the better the result.

Color fastness to light (JIS L 0842, JIS L 0843)
The "Color fastness to light test" is a test for evaluating discoloration/fading (color change) due to the effect of light. Light has the effect to cause fading. There are two types of testing method; ultraviolet carbon arc light (JIS L 0842) that mainly irradiates ultraviolet rays, and xenon arc light (JIS L 0843) that irradiates light similar to sunlight. Ultraviolet carbon arc lamps are the mainstream in Japan, and xenon arc lamps are the mainstream overseas.
The general standard criteria for clothing are change of color class 3 or higher.
In addition, ISO105-B02, AATCC 16.3, etc. can be tested.


Color fastness to Washing (JIS L 0844)
The "Color fastness to washing test" is a test that evaluates discoloration/fading (color change) and color transfer (staining) to other laundry" due to the effect of washing at home. According to JIS L 0844 A-2, washing is done using 0.5% detergent solution at 50 ℃ for 30 minutes.
The general standard criteria for clothing are change color class 4 and above, and staining class 3 and above.
In addition, ISO105-C06, AATCC61, etc. can be tested.

Color fastness to perspiration (JIS L 0848)
The "color fastness to perspiration test" evaluates "discoloration/fading (color change) " and "color transfer (staining) to other layered shirts" due to the effect of sweat(perspiration). The test specimen is impregnated with an acidic or alkaline artificial perspiration solution and treated at 37℃ for 4 hours with a load of about 12.5 kPa.
The general standard criteria for clothing are change color class 4 and above, and staining class 3 and above.
In addition, ISO105-E04, AATCC15, etc. can be tested.
Color fastness to rubbing (JIS L 0849)
The "Color fastness to rubbing test" evaluates "color transfer (staining) to other layered shirts" due to the effect of rubbing. In JIS L 0849 type II method, a dry cotton cloth or a water-moistened cotton cloth is rubbed back and forth against the test specimens 100 times with a load of 2N.
The general standard criteria for clothing are class 3-4 and above in dry condition, and class 2 and above in wet condition.
In addition, ISO105-X12, ISO105-X19, AATCC8, GB / T3920, etc. can be tested.

Color fastness to Dry cleaning (JIS L 0860)
The "Color fastness to Dry cleaning test" is a test that evaluates “discoloration/fading (color change)” and “color transfer (staining) to other laundry" due to the effect of dry cleaning. The JIS L 0860 A-1 method uses a test solution that is a mixture of perchloroethylene, surfactant, and water. 20 stainless steel balls are put in the testing solution and washed at 30℃ for 30 minutes.
B-1 method uses a test solution that is a mixture of petroleum-based solvent, surfactant, and water. 20 stainless steel balls are put in the testing solution and washed at 30℃ for 30 minutes.
The general standard criteria for clothing are change color class 4 and above, and staining grade 3 and above.
In addition, ISO105-D01, AATCC132, etc. can be tested.

Physical properties
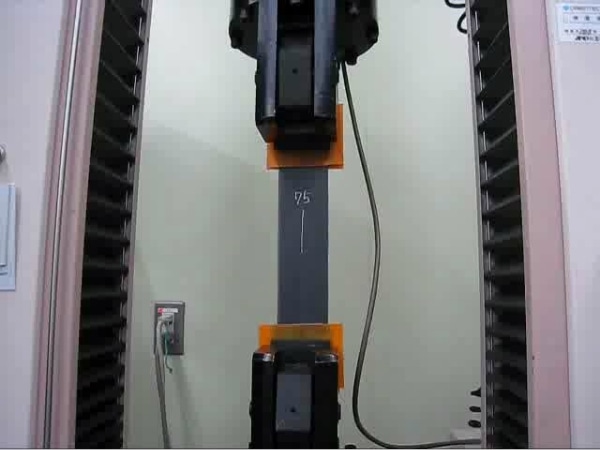
Tensile strength test (JIS L 1096)
The "tensile strength test" evaluates the strength at which a woven fabric breaks when pulled. In the JIS L 1096A Method A (Strip method), a test specimen with a width of 50 mm and distance of 200 mm in between clamps is pulled at a speed of 200 mm/min using a tensile strength tester.
The general standard value for clothing is 200N or higher.
In addition, JIS L 1096 Method B (Grab method), ISO13934-1, ISO13934-2, etc. can be tested.

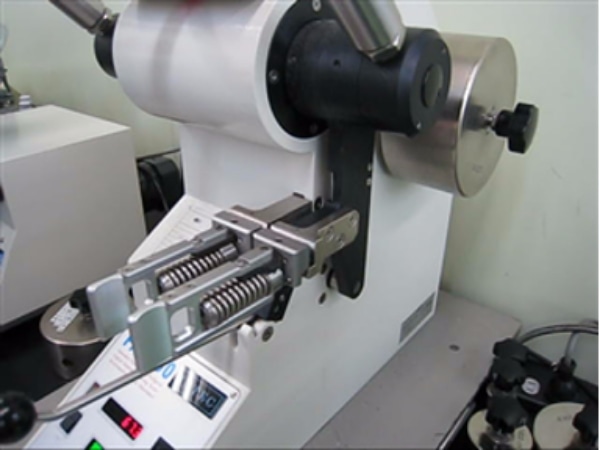
Tearing strength test (JIS L 1096)
The "Tearing strength test" evaluates the strength at which woven fabrics break when they are torn. In the JIS L 1096 Method D (Pendulum method), a cut is made in the test specimen and is torn by the force of a pendulum using a tearing tester.
The general standard criteria for clothing are 7N or more for thin fabrics and 10N or more for thick fabrics.
In addition, JIS L 1096 Method A-1 (Single tongue method), ISO 13937-1 etc. can be tested.

Bursting strength test(JIS L 1096)
The “Bursting strength test" evaluates the strength at which a knitted fabric is broken when ruptured. In JIS L 1096 Method A (Mullen type), a rubber film is hydraulically inflated from the back side of the test specimen until it bursts.
The general criter1a for clothing are 300 kPa or more for thin fabrics and 400 kPa or more for thick fabrics.
In addition, ISO13938-2, ASTM D3786, etc. can be tested.
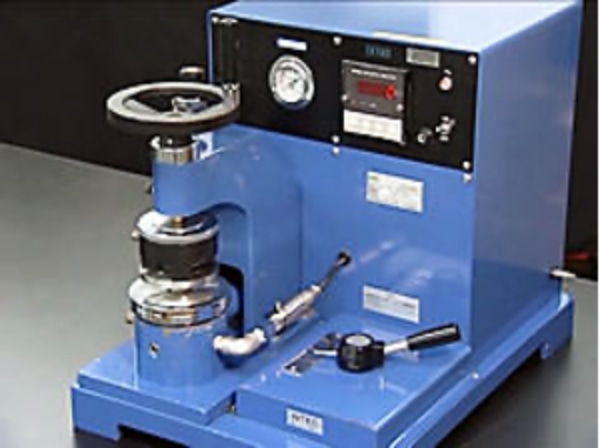

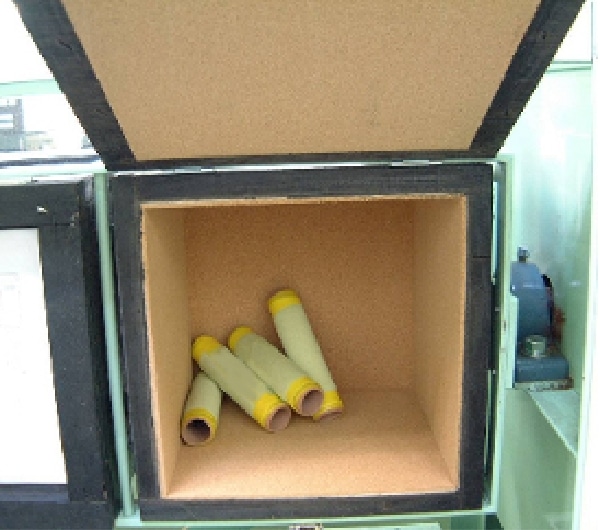
Pilling test (JIS L 1076)
The "Pilling test" evaluates the degree of pilling caused by friction when worn and washed. In the JIS L 1076 Method A (ICI type testing machine method), four test specimens are wrapped around four special rubber tubes respectively and placed in a box with cork plates attached on six sides. The box is rotated for 10 hours for woven fabrics and 5 hours for knitted fabrics and then the tested specimens are compared to standard photos for judgement.
The general criteria value for clothing is grade 3.0 or higher.
In addition, JIS L 1076 C method (ART method), ISO12945-1, ISO12945-2, etc. can be tested.


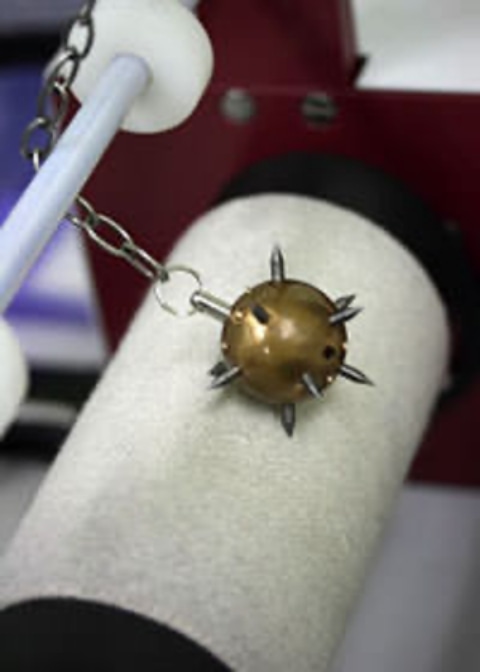
Snagging test (JIS L 1058)
The "Snagging test" evaluates the phenomenon in which fibers and threads protrude from the surface of the fabric and cause twitching. In the JIS L 1058 Method A (Mace method), a cylindrical test specimen is attached to the cylinder of the testing machine and the cylinder is rotated while a sphere with spikes (mace) bounce on the test specimen. After rotating 100 times, the tested specimens are compared to standard photos for judgement.
The general criteria value for clothing is grade 3.0 or higher.
In addition, JIS L 1058 D-1 method (Damage stick method), ASTM D3939, etc. can be tested.

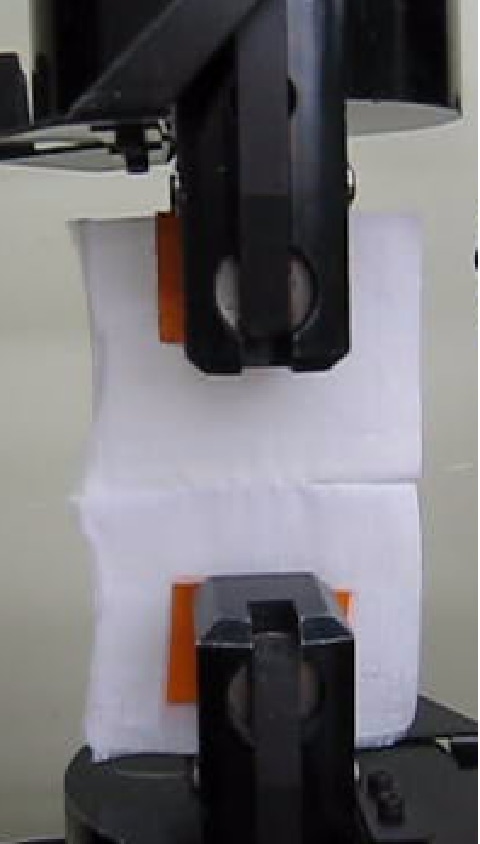
Seam slippage test
The "Seam slippage test" is a test to evaluate whether the threads near the seam will slip when a force is applied. In JIS L 1096 Seam slippage Method B, two pieces of fabric are overlapped and lock sewn 10 mm from the edge. Placing the seam in center, the fabric is pulled using a tensile tester with a load of 49N for thin fabrics and 117.7N for thick fabrics, and then the sliding distance of the thread at the seam is measured.
The general standard criteria value for clothing is 3.0 mm or less.
In addition, ISO13936-1, ASTM D434, etc. can be tested.

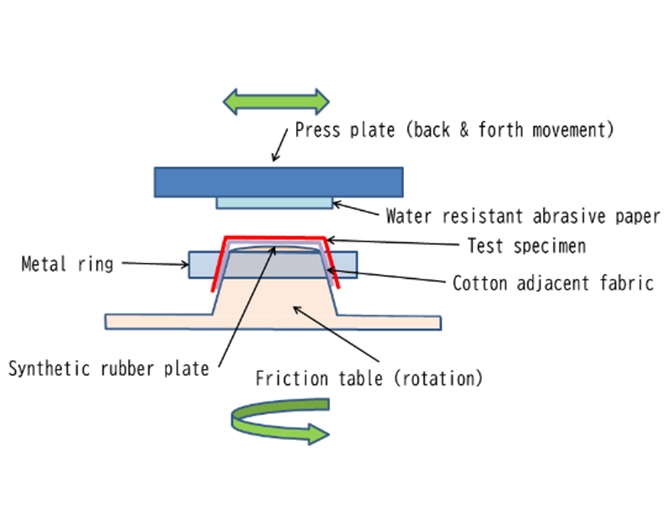
Pile retention test (Kaken method)
The "Pile retention test" is a test to evaluate the degree of defluxion of pile yarn.
In the Kaken method, which is often used in Japan, test specimen is placed to a universal abrasion tester with the piles facing downward. A constant load is applied while the back side of the pile fabric is rubbed using water-resistant abrasive paper. Test is done a specified number of times and series until the pile falls off to the same extent as the standard photo.
The general criteria value for clothing are 300 times or more and 3-4 grade or more.
In addition, JIS L 1075 A method, JIS L 1075 B method, etc. can be tested.
Dimensional change rate of fabrics
Soap liquid immersion method (JIS L 1096 Method D)
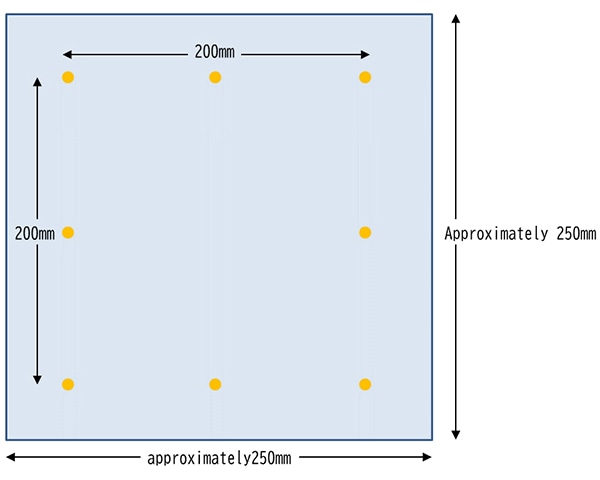
“Soap liquid immersion dimensional change rate" evaluates the dimensional change after static treatment in warm water containing detergent. 200mm point is marked on a test piece of approximately 250 mm x 250 mm. The test specimen in immersed in 50 ℃ warm aqueous solution of 0.5% soap for 20 minutes. After flat-drying the dimensional change rate is measured and calculated.
Dimensional change rate (%) =
{(Length after treatment (mm) -Length before treatment (mm)) / Length before treatment (mm)} x 100
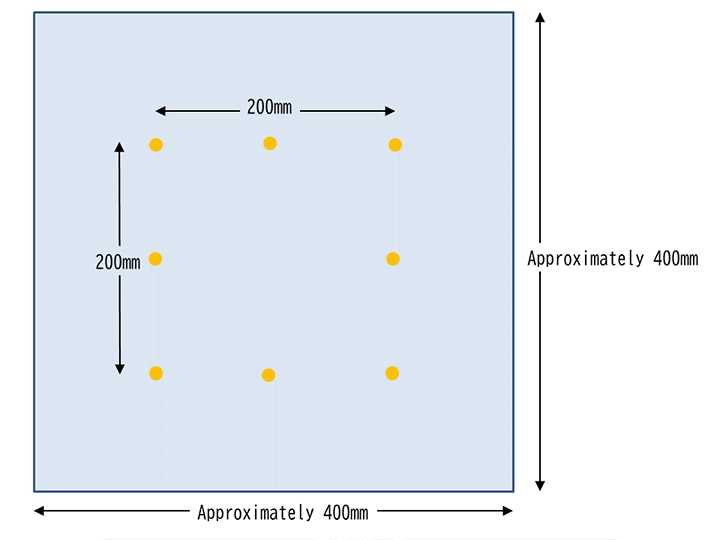
Domestic electric washing machine method (JIS L 1096 Method G)
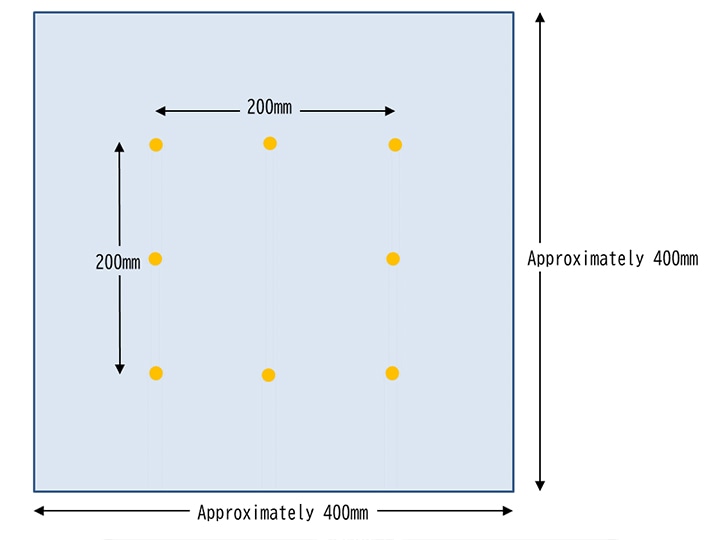
“Domestic electric washing machine dimensional change rate" evaluates the dimensional change after wash using a home washing machine. 200mm point is marked on the test specimen - one piece of about 400 mm x 400 mm for woven fabrics and a double-layered test piece of approximately 300 mm x 300 mm for knitted fabrics.
Wash, rinse 2 times and dehydrate based on JIS L 1930 Method C4M (synthetic detergent washing liquid concentration 0.133%, water temperature 40℃). After hang-drying, flat-drying or tumble-drying, the dimensional change rate is measured.
Dimensional change rate (%) =
{(Length after treatment (mm) -Length before treatment (mm)) / Length before treatment (mm)} x 100
The general criteria for clothing are woven fabrics within ± 3% and knitted fabrics + 3 to -6%.
Hot Pressing method (Steam open method) (JIS L 1096 Method H-2)
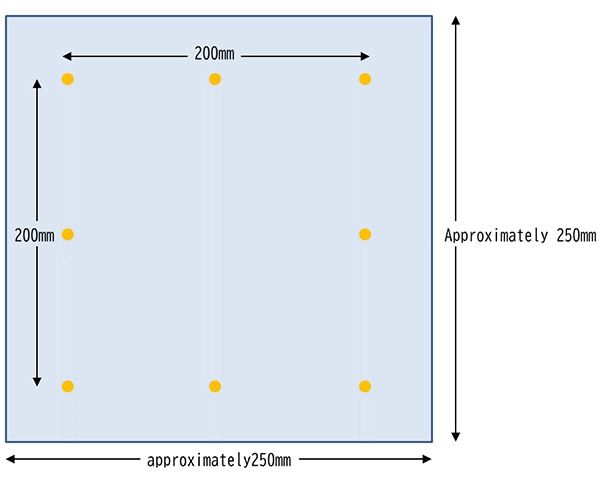
“Steam open press dimensional change rate" evaluates the dimensional change when performing steam treatment used for finishing textile products. 200mm point is marked on a test specimen of approximately 250 mm x 250 mm. Steam is applied for 15 seconds at a position about 20 mm from the surface of the fabric, then suctioned for 15 seconds to measure the dimensional change rate.
Dimensional change rate (%) =
{(Length after treatment (mm) -Length before treatment (mm)) / Length before treatment (mm)} x 100
The general criteria for clothing are within ± 3%.
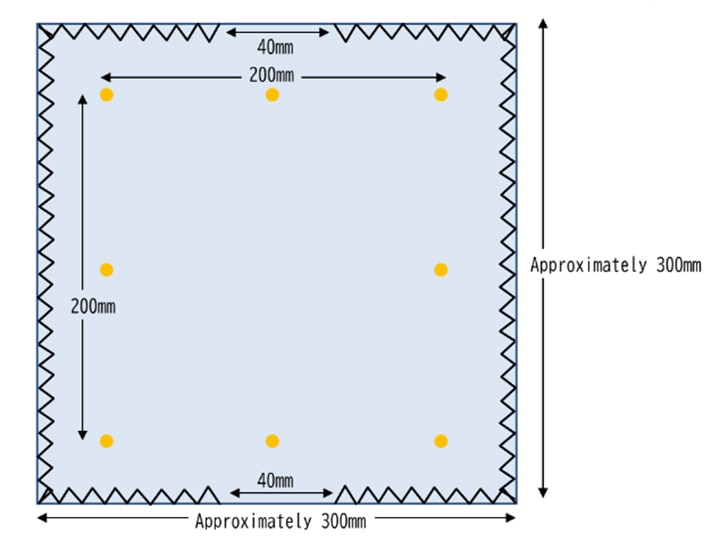
Dry cleaning method (JIS L 1096 Method J)
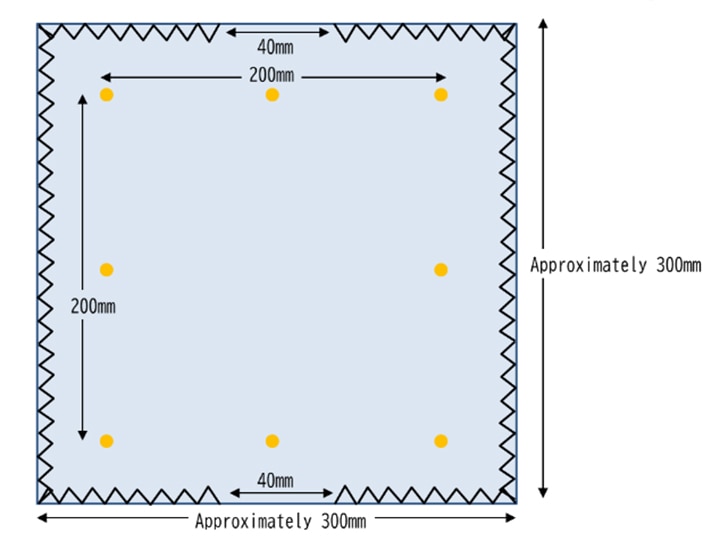
“Dry cleaning dimensional change rate" evaluates the dimensional change after cleaning with a wash cylinder. For woven fabrics, one piece of about 250 mm x 250 mm is used, and for knitted fabrics, a double-layered test piece of approximately 250 mm x 250 mm is used and the 200mm point of the specimens are marked.
The JIS L 1096 J-1 method uses perchloroethylene solvent and the JIS L 1096 J-2 method uses a petroleum-based solvent. The dimensional change rate is measured after treatment for a certain period of time.
Dimensional change rate (%) =
{(Length after treatment (mm) -Length before treatment (mm)) / Length before treatment (mm)} x 100
The general standard value for clothing is within ± 3%.
Inspection of textile products
Labeling items
Textile products such as clothing sold in Japan are required by law to have the following labels (excluding size labels), and to make sure that they are labeled correctly.
- Household Goods Quality Labeling Law (Japanese Law No.104)
- Indication of fiber composition
- Indication of handling methods such as home washing
- Indication of Water repellency
- Act against Unjustifiable Premiums and Misleading Representations (Japanese Act No. 134))
- Indication of Country of origin
- Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS)
- Indication of Size(Optional labelling)
Appearance / Sewing
Making sure the textiles products such as clothing are produced correctly for use.
- Materials used (fabric defects, cracks on buttons, zippers, prints, etc.)
- Appearance of the entire product (distortion, symmetry, pattern matching, brushing direction, etc.)
- Sewing specifications (sewing condition of each part, neck extension dimension, reinforcement of parts where force is applied, etc.)
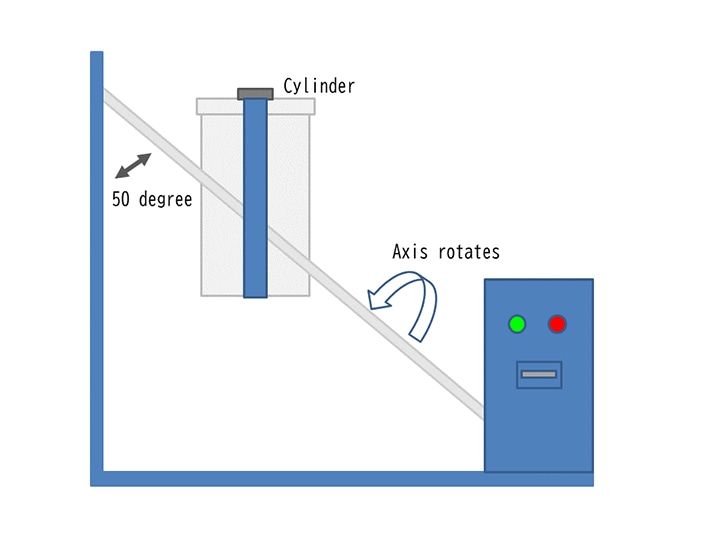
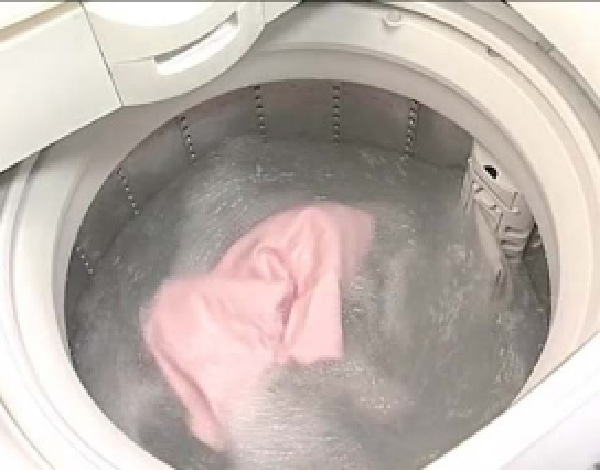
Durability against washing, Durability against dry cleaning
Washing with water or dry cleaning according to the handling label indicated on textile products such as clothing, and checking whether any problems occur.
- Change in appearance
- Change in sewn parts
- Color change (discoloration / fading, bleeding)
- Puckering
- Twisting
- Dimensional change (expansion / shrinkage)


Shoes / Bag / Umbrella
Shoes / Peeling strength of outsole (JIS T 8101 modified)
"Peeling strength of the outsole" evaluates the difficulty of peeling between the outsole (the part in contact with the ground) of the shoe and the instep. Using a tensile tester, the sole is peeled starting from the toe part and the average and minimum strength is measured.
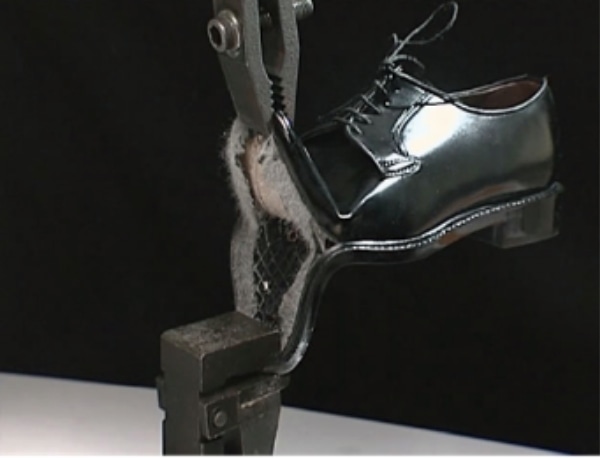

Shoes / Impact strength test of heels
"Heel impact strength test" evaluates the strength of the heel of a shoe when impact is applied. An impact with a force of 22J is applied with a hammer at a position 10mm from the heel’s contact surface and the maximum absorbed energy that damages the heel is measured.
In addition, ISO 19956, ISO 19953, etc. can be tested.

Bag / handle・shoulder strap mounting strength test (JIS L 1096 Method A modified)
The "handle・shoulder strap attachment strength test" evaluates whether the bag handle and shoulder strap attachment are strong enough for the load during use.
The handle and its mounting part are grasped with a tensile tester and pulled. The load of when it breaks will be measured.

Bag / Seam strength of bottom part (JIS L 1093 Grab method・A-1 method)
The “seam strength of bottom part test" evaluates whether the bag’s bottom stitches or the gusset stitches are strong enough against the load when items are put in the bag. The bottom or gusset seams are pulled with a tensile tester and the maximum load at the time of breakage is measured.

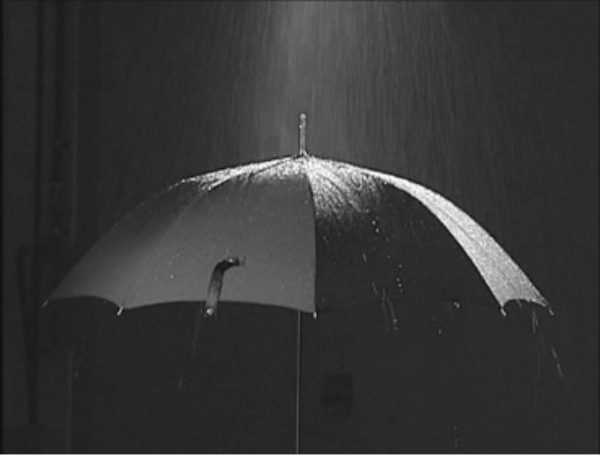
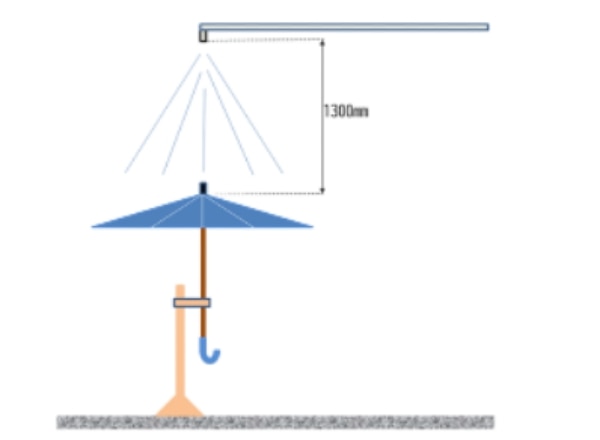
Umbrella / Leakage resistance test (JIS S 4020: 1994)
"Leakage resistance test" evaluates the leaking condition of an umbrella. Using an artificial rainfall tester, the umbrella is tested for 20 minutes at a rainfall of 20 mm/h. The inside of the umbrella is checked for water transmission and water droplets.

Functionality
Water absorption and quick-drying test (JIS L 1907, ISO 17617)
The “Water absorption and quick-drying test" evaluates the ability to absorb and diffuse sweat for the fabric to dry quickly. Water absorption test and quick-drying test are performed as a set. In the JIS L 1907 Dripping method of the water absorption test, one drop of water is dropped from the burette and the time until the water drop is absorbed by the fabric is measured. In the ISO 17617 Method A-1 of the quick-drying test, the weight of the test specimen is measured immediately after dropping 0.3 ml of water on the test piece. The rate (%) of the moisture that dries is measured then an approximate expression (y = ax + b) is calculated. When y = 100 in the approximate expression, x is evaluated as the drying time (100%), and the inclination of the approximate equation is evaluated as the drying rate [DR].
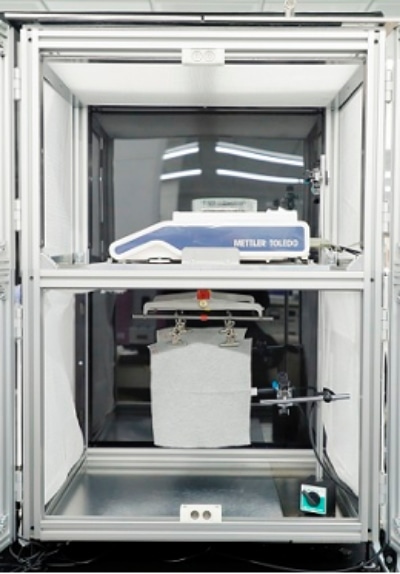
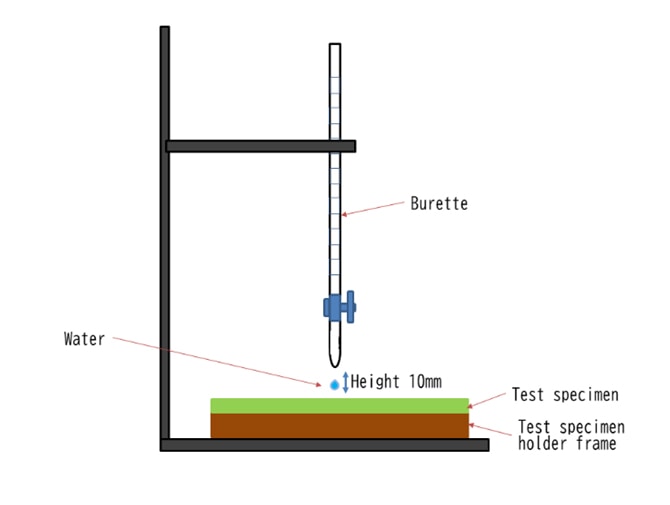

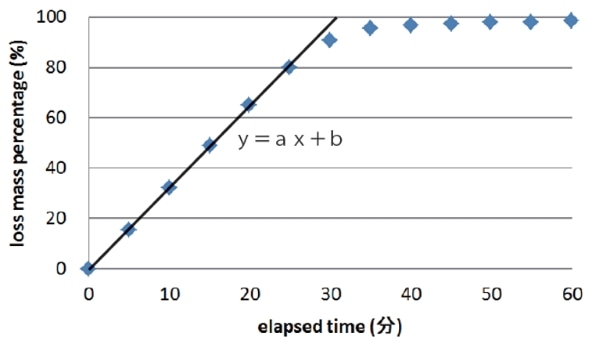
Hygroscopic heat generation test (JIS L 1952-1, ISO18782)
The “Hygroscopic heat generation test" evaluates the function of giving a feeling of warmth by using the heat generated when water molecules in the air are adsorbed in fibers. After bringing the test specimen to low humidity (20℃, 40% RH), high humidity (20℃, 90% RH) air is supplied. The maximum generated hygroscopic heat temperature (ΔTmax) is measured.
Note: The maximum generated hygroscopic heat temperature (ΔTmax) is the peak temperature (Tpeak) minus the initial temperature (Tinitial).
This test was developed at the Kaken Test Center.
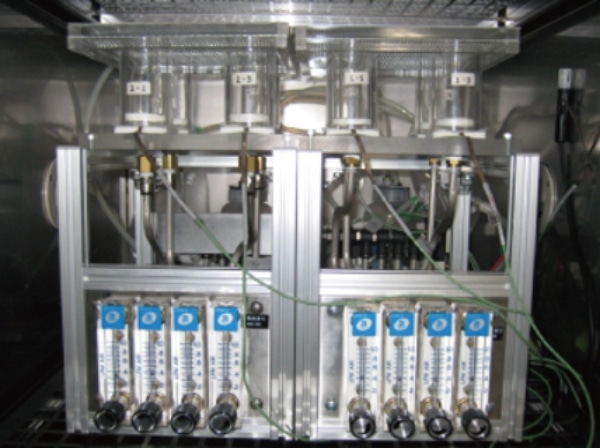

Water repellency test (JIS L 1092)
The “Water repellency test" is a test that evaluates the waterproof performance of the fabric by repelling water. In the JIS L 1092 spray method, 250 mL of water is sprayed on the test specimen and evaluated on 5 Grades.
Grade 5: No wetness, no water droplets
Grade 4: No wetness, small water droplets adhered
Grade 3: Small water droplet-like wetness
Grade 2: About half moist
Grade 1: Overall moist
In addition, ISO 4920, AATCC 22, etc. can be tested.
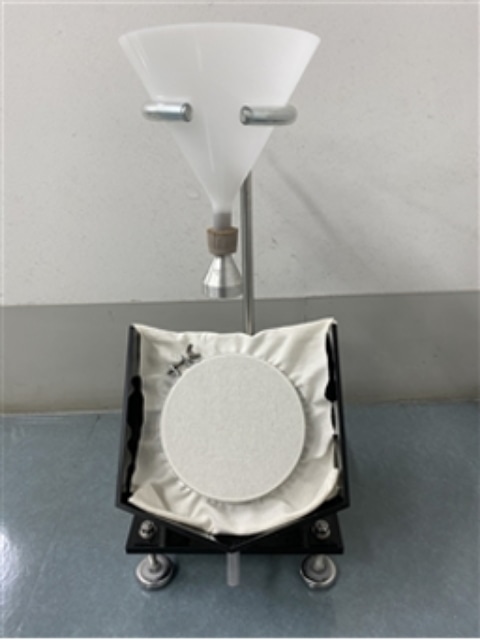
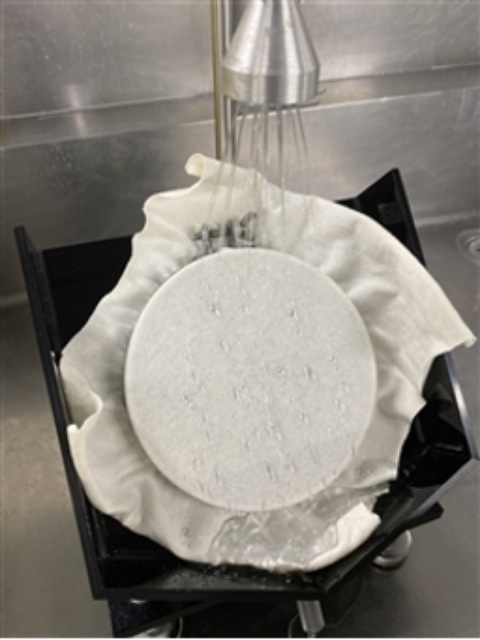


Water resistance test (JIS L 1092)
The “Water resistance test" evaluates how much water leaks out when water pressure is applied to the fabric. In the JIS L 1092 Method A, water pressure is applied to the test piece at a speed of 600 mmH2O or 100 mmH2O for 1 minute, then the water pressure of when 3 drops of water leaks out of the test specimen is measured.
In addition, JIS L 1092 Method B, ISO 811, AATCC 127, etc. can be tested.
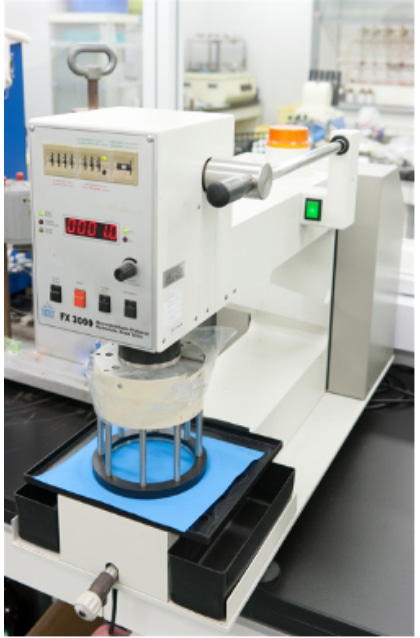

Heat retention test (JIS L 1096)
The “Heat retention test" evaluates the difficulty of heat release. In the JIS L 1096 Method A, a test specimen is placed on a heat source at about 36℃, and the amount of heat loss dissipated within the testing machine after 2 hours is calculated. The heat retention rate is calculated by comparing with the amount of heat loss when the test specimen is not placed.
Other tests such as ASTM D 1518 are possible.
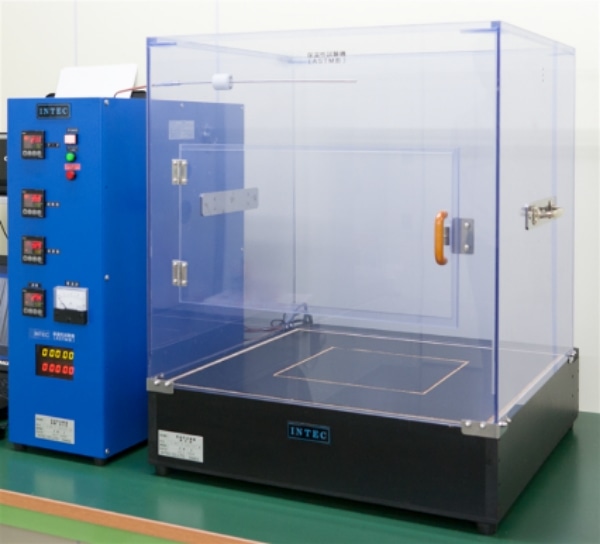

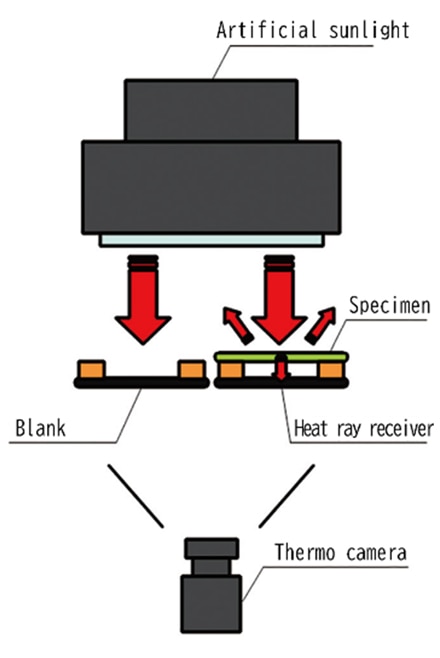
Heat-ray shielding test (JIS L 1951)
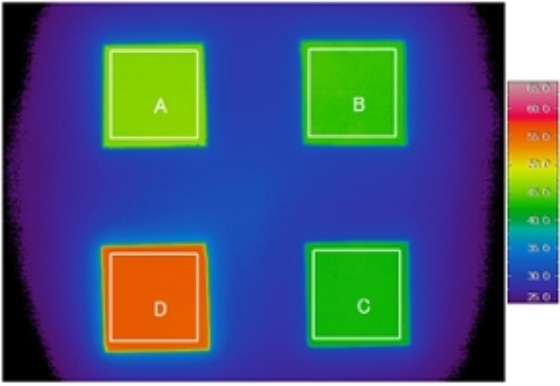
The "Heat-ray shielding test" evaluates the ability of the fabric to suppress the temperature rise by blocking the radiant heat generated by sunlight. The test specimen is irradiated with artificial sunlight, and the radiant heat that has passed through the test specimen is absorbed by the heat ray receiver.
After 30 minutes of irradiation, the rise of temperature of the heat ray receiver attached to the test specimen and the blank heat ray receiver is measured with a thermo camera.
The Heat-ray shielding rate is calculated from the rising temperature of the blank and that of the test specimen.

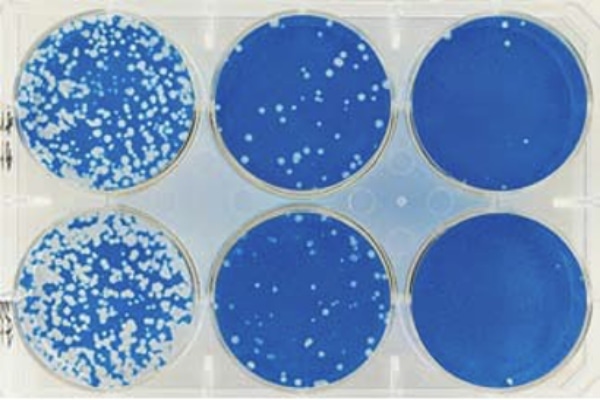
Antiviral test of textile products (JIS L 1922)
The “Antiviral test" evaluates the degree to which the infectious titer of the virus attached to the textile product decreases.
After inoculating the antiviral test specimen and standard fabric with the virus solution, it is let stand at 25℃ for 2 hours. The virus infectivity is measured by the plaque method, and the antiviral activity value is calculated. The plaque method is a method for measuring the amount of virus that utilizes the degeneration of cells infected by the virus. Influenza A virus and feline calicivirus are used as virus species.
In addition, ISO 18184 etc. can be tested.
Antiviral test for plastic products (ISO21702)
“Antiviral test" is to evaluate the degree of decrease in the infectious titer of the virus adhering to plastic products. After inoculating the anti-virus processed and unprocessed test specimens with the virus solution, they are covered with a film and is let stand at 25 ℃ for 24 hours. The virus infectivity is measured by the plaque method, and the antiviral activity value is calculated. The plaque method is a method for measuring the amount of virus that utilizes the degeneration of cells infected with the virus. Influenza A virus and feline calicivirus are used as virus species.
Antibacterial test of textile products (JIS L 1902)
The "Antibacterial test" evaluates the degree to which the viable cell counts of bacteria adhering to textile products decreases.
In the JIS L 1902 bacterial solution absorption method, the bacterial solution is inoculated into both the test specimen and standard fabric, and cultured at 37 ℃ for 18 hours. After culturing, the bacterial solution is washed out, the viable cell counts are counted by the poured-plate culture method, and the antibacterial activity value is calculated. Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, etc. are used as the bacterial species.
In addition, ISO 20743 etc. can be tested.
Antibacterial test for plastic products (JIS Z 2801)
The "antibacterial test" evaluates the degree to which the viable cell counts of bacteria adhering to plastic products decreases.
After inoculating the bacterial solution into a flat plate-shaped antibacterial test specimen and an unprocessed test specimen, they are covered with a film and incubated at 35 ° C and 90% RH for 24 hours. After culturing, the bacterial solution is washed out, the viable cell counts are counted by the poured-plate culture method, and the antibacterial activity value is calculated. Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli are used as the bacterial species.
In addition, ISO 22196 etc. can be tested.
Deodorant test (SEK mark textile product certification standard)
The “Deodorant test" evaluates the function that reduces the intensity of odor by reducing the concentration of odorous components around the fiber.
In the detector tube method, a test specimen and a gas to be measured (ammonia, acetic acid, etc.) are placed in a sampling bag, then the gas concentration is measured with the detector tube after a certain period of time, and the reduction rate is calculated. In the gas chromatograph method, a test specimen and a solution to be measured (isovaleric acid, nonenal, etc.) are placed in an Erlenmeyer flask, and after a certain period of time, measurement is performed with a gas chromatograph and the rate of decrease is calculated.
In addition, ISO17299-2 etc. can be tested.


Ultraviolet(UV) ray shielding test (JIS L 1925)
The "Ultraviolet ray shielding test" evaluates the degree of shielding ultraviolet rays by kneading a substance that absorbs or reflects ultraviolet rays (titanium oxide, aromatic compounds, etc.) into fibers or applying it on the surface of fibers. Using a spectrophotometer, the transmittance for ultraviolet rays with a wavelength of 290 to 400nm is measured, then the ultraviolet shielding rate is calculated.
In addition, AS / NZS 4399, AATCC 183, etc. can be tested.

Electrostatic propensity test (JIS L 1094)
"Electrostatic propensity test" is to evaluate the degree of prevention of static electricity by kneading antistatic agent into fibers, applying antistatic agent on the surface of fibers, or using conductive fibers. In JIS L 1094 Method B(Friction-charged electrostatic potential measuring method), the electric charge amount generated by rubbing the test specimen against wool (or cotton) is measured.
In addition, JIS L 1094 Method A / Method C, JIS T 8118, ISO 18080, IEC61340-5-1 TR2, etc. can be tested.

Safety evaluation
Flammability test (JIS L 1091)
“Flammability test" evaluates the function that makes it difficult to ignite when heated by an initial fire and slows down the speed at which it spreads even after ignition. In the JIS L 1091 Method A-1, flame is applied from below with the test specimen tilted at 45 degrees, then the extent of combustion spread (combustion area and combustion length), residual flame and length of afterglow time is measured.
In addition, JIS L 1091 Method A-2 / Method A-4 / Method E, 16CFR Part1610, FMVSS302, UL94, FAR, etc. can be tested.

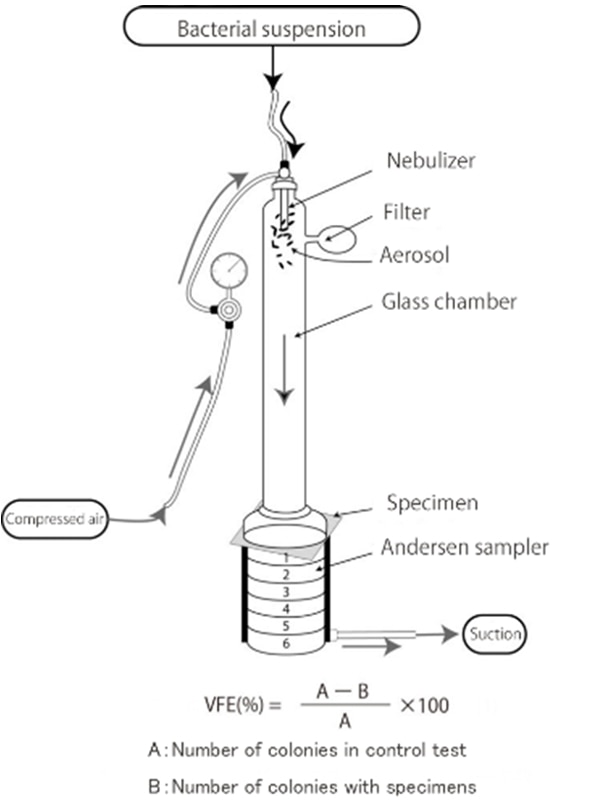
Bacterial Filtration Efficiency(BFE) test (JIS T 9001)
“Bacterial Filtration Efficiency test" evaluates the ability to collect (filter) bacteria through the non-woven fabric of medical masks and general-purpose masks. Bacterial droplet collection efficiency is calculated by passing an aerosolized bacterial turbid solution (particle size 3.0μm) with and without the test specimen filter.
Other tests such as ASTM F2101 are also available.
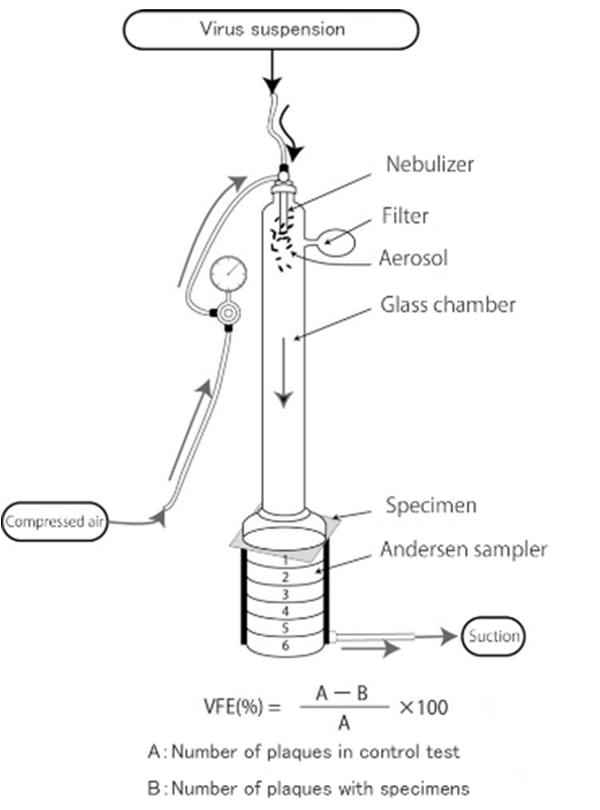
Viral Filtration Efficiency (VFE) test (JIS T 9001)
The “Viral Filtration Efficiency test" evaluates the ability to collect (filter) bacteria through the non-woven fabric of medical masks and general-purpose masks. The aerosolized virus turbid solution (particle size 3.0μm) is passed through with and without the test specimen filter, then the virus droplet collection efficiency is calculated. This is a test method developed by Kaken Test Center.
Sub-micron Particulate Filtration Efficiency (PFE) test (JIS T 9001)
The “sub-micron particulate filtration efficiency test" evaluates the ability of filter material such as a mask to collect (filter) sub-micron test particulates. While sucking polystyrene latex particles with a particulate size of 0.1μm at a constant flow rate, the number of particulates on the upstream and downstream sides of the filter test specimen is counted to calculate the sub-micron particulate collection efficiency.
Other tests such as ASTM F2299 are also available.

Resistance of masks to penetration by synthetic blood (JIS T 9001)
“Resistance of masks to penetration by synthetic blood " is a test to evaluate the barrier property (penetration resistance) of medical masks to synthetic blood. The synthetic blood is sprayed onto the mask at the specified pressure. The injection pressure is 10.6kPa (80mmHg), 16.0kPa (120mmHg) and 21.3kPa (160mmHg). After injection, the inner side of the mask is observed for 10 seconds to visually check for the presence or absence of synthetic blood penetration.
Other tests such as ASTM F1862 are possible.
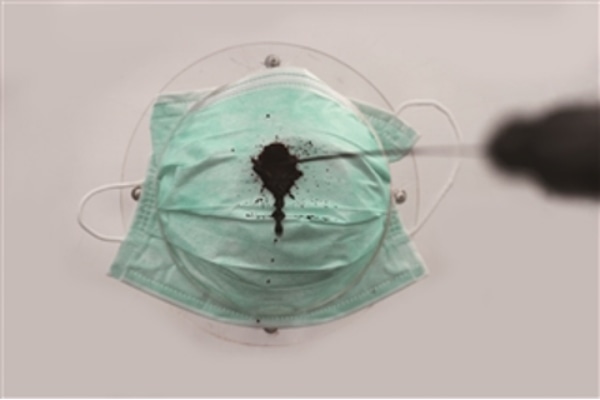
Resistance of protective clothing materials to penetration by synthetic blood/ by Synthetic blood penetration resistance test of masks (JIS T 8060 / JIS T 8061)
The "Synthetic blood/ Synthetic blood penetration resistance test of protective clothing materials" mainly targets protective clothing worn by healthcare professionals as a countermeasure against infectious diseases, and evaluates whether blood or viruses permeate the protective clothing. In the synthetic blood barrier test, a test piece is attached to the test cell, then a predetermined pressure is applied to the synthetic blood, and the presence or absence of permeation of the synthetic blood on the inner side of the fabric is visually judged. In the virus barrier test, a test piece is attached to the test cell, then a predetermined pressure is applied to the virus suspension. Permeated virus suspension that passed through to the inner side of the fabric is extracted by neutralizer, and the presence or absence of plaque is checked.
In addition, ASTM F1670, ASTM F1671, ISO16603, ISO16604, etc. can be tested.

Protective gloves to cut resistance and other mechanical risks (EN 388: 2016 (ISO 23388: 2018) / JIS T 8052 (ISO 13997: 1999))
The “Protective gloves to cut resistance and other mechanical risks" test is to evaluate the cut resistance of gloves used at work sites that requires use of blades such as cutters. There are two methods for cut resistance test, the Coupe test and TDM test. In the Coupe test, a round testing blade reciprocates over a movement distance of 50 mm while rotating. The number of round trips are measured until the sample is penetrated, and the index value is obtained. The TDM test estimates the incision force (N) required for the test blade to move 20 mm and penetrate the test piece.


Analytical test
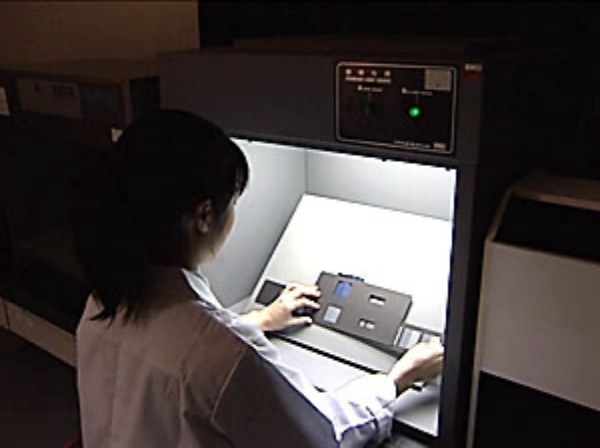
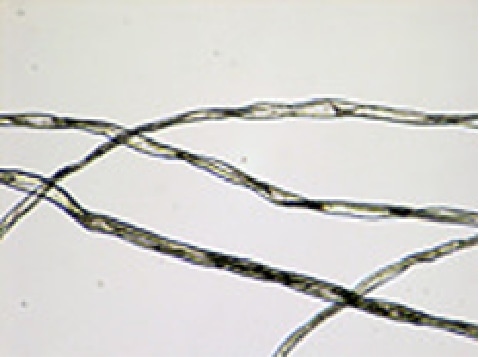
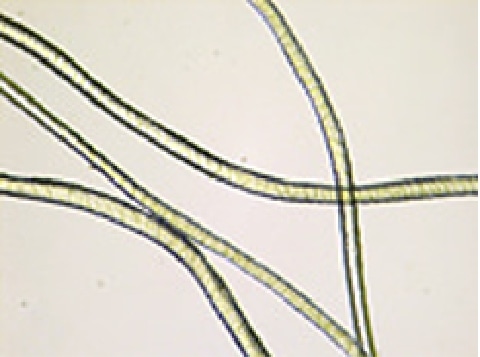
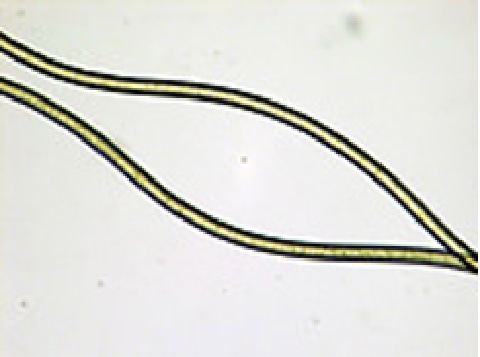
Fiber identification / Mixture ratio (JIS L 1030)
"Fiber identification / Mixture ratio" is a test to identify the type of fibers and examine the ratio of each mixed fiber. In the fiber identification test, the type of fiber is identified by the appearance of the fiber, solubility in reagents, infrared spectrophotometer, etc. In the mixture ratio test, the mixing ratio of each fiber is determined by release method, dissolution method (using reagents), microscopic method (observing appearance), etc.
Photos under microscope
Free formaldehyde test for textile products (JIS L 1041, Ministry of Health and Welfare Ordinance No. 34)
The "Free formaldehyde test" evaluates the amount of formaldehyde contained in the fiber that is released by liquid phase extraction. Formaldehyde has antiseptic and anti-bactericidal effects, and is used in textile products for wrinkle-proofing and shrink-proofing process. However, its use is restricted due to its impact on the human health.In JIS L 1041 Method A, 2.5 g of test specimen is extracted with warm water at 40 ℃, then acetylacetone reagent is added to the extract to develop color. The content of free formaldehyde in the colored solution is measured using a spectrophotometer.

Analysis of certain aromatic amines (JIS L 1940-1 / JIS L1940-3)
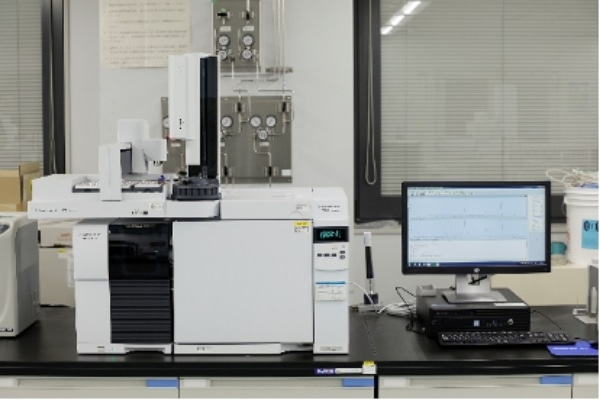
When azo dyes with azo groups are reduced and decomposed, certain aromatic amines, which have been pointed out to be carcinogenic, may be produced. There are 24 types of certain aromatic amines such as benzidine (CAS No. 92-87-5), and their contents are measured by gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer (GC-MS) or high-performance liquid chromatograph (HPLC-MS).
In addition, Japanese Law No. 112, EN14362-1, EN14362-3, ISO17234-1, ISO17234-2, GB / T 17592, GB / T 23344, etc. can be tested.


